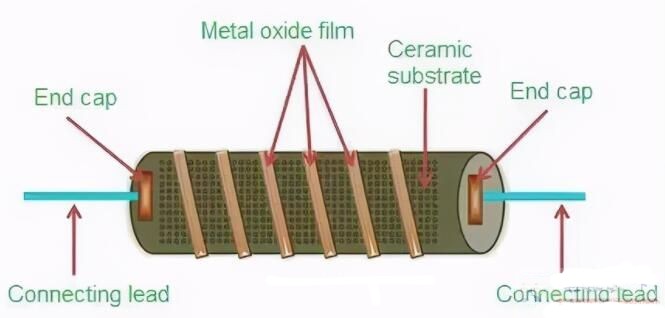
Metal oxide film resistors are resistors that use special metals or alloys as resistive materials, and use vacuum evaporation or sputtering methods to basically form an oxidized resistive film layer on ceramics or glass.
The metal oxide film is to form a layer of tin oxide film on the ceramic rod. In order to increase the resistance, a layer of antimony oxide film can be added on the tin oxide film, and then a spiral groove is processed on the oxide film to precisely control the resistance. .
The biggest advantage of metal oxide film resistors is high temperature resistance.
The main parameters:
1. Nominal resistance value: The nominal resistance value on the resistor is called the nominal value. Unit: Ω, kΩ, MΩ, the nominal value is marked according to the standard series formulated by the country, not arbitrarily calibrated by the manufacturer, and not all resistors with resistance values exist.
2. Allowable error: The maximum allowable deviation range of the actual resistance value of the resistor from the nominal value is called the allowable error. Error codes: F , G , J, K… (Common error ranges are: 0.01[[%]], 0.05[[%]], 0.1[[%]], 0.5[[%]], 0.25[[% ]], 1[[%]], 2[[%]], 5[[%]], etc.)
3. Rated power: It refers to the allowable power consumption on the resistor under the condition of the specified ambient temperature, assuming that the surrounding air is not circulating, and the resistor will work continuously for a long time without damage or basically change the performance of the resistor. Common ones are 1/16W, 1/8W, 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, 2W, 5W, 10W.

